MySQL参数autocommit生产环境设1还是0?为什么?
MySQL参数autocommit生产环境设成0,即不自动提交。 设置成不自动提交,事务能做rollback,以满足事务的原子性Atomicity的要求,设置方法:set autocommit=0;
# 也可以修改my.cnf配置文件
autocommit=0
MySQL参数tx_isolation生产环境上大多数是设什么值,为什么?
MySQL参数tx_isolation生产环境上大多数是设成READ-COMMITED。事务的隔离级别设置为READ-COMMITED时不会发生脏读现象,虽会出现不可重复读和幻读问题,但不会对业务应用造成影响。而设置成以下隔离级别会出现的问题如下:
- Read Uncommitted:会产生脏读、不可重复读、幻读现象,而脏读这在生产环境中是不被允许的
- Repeatable Read:不会出现不可重复读和幻读问题,但此特性一般不符合应用业务需要,且并发性能也不好。
- Serializable:所有事务全部串行执行(只允许同时一个事务操作,若有其他事务,也需要等前一个事务完成后才能开始),不能并发执行,这在生产环境中是不现实的。
与MySQL锁相关的有哪些因素?
- 有无主键
- 有无索引,是不是唯一索引
- 事务的隔离级别是什么
- SQL语句的执行计划
课堂笔记
事务的概念
事务定义了一个服务操作的序列,由服务器保证这些操作序列在多个客户并发访问和服务器出现故障情况下的原子性。
事务概念最初是在数据库管理系统领域发展起来的,是一种对共享数据库进行并发访问或错误处理的范型。
A transcation consists of a collection of DML statements that form a logical unit of work.
DDL statements will implicitly commit any outstanding transcation.
事务的属性 ACID
Atomicity: Changes made by a transaction to the database are atomic, “all or nothing”. [Redo & Undo]Consistency: The transaction changes the state of the base from one coherent state to a new coherent state (conforming to integrity constraints). [Undo]Isolation: The transaction is isolated from other transactions and appears to be the only user on the system even though it is executing with other concurrent transaction. [lock]Durability(Durable): The committed changes by a transaction are persistent, capable of surviving machine crashes. [Redo]
并发会存在问题
- dirty read 脏读
- unrepeatable read 不可重复读
- phantom read 幻读
事务的隔离级别
- Read Uncommitted:会出现脏读、不可重复读、幻读(隔离级别最低,并发性能高)
- Read Committed:会出现不可重复读、幻读问题(锁定正在读取的行),Oracle的默认隔离级别
- Repeatable Read:会出幻读(锁定所读取的所有行),Mysql的默认隔离级别,在Mysql Innodb上设置此隔离级别幻读也不会产生
- Serializable:保证所有的情况不会发生(锁表)
事务编程不好习惯
- 在循环中提交:提交
commit应尽量放到循环外 - 使用自动提交:不使用自动提交,
set autocommit=0 - 使用自动回滚:MSSQL中关闭自动回滚
- 大事务:尽量拆成小事务
锁的概念
什么是锁
锁用于在多个事务访问同一个对象时根据这些操作访问同一对象的先后次序给事务排序。
不同数据库的锁实现
- InooDB 行级锁
- Oracle 行级锁
- MyISAM 表锁
- Microsoft SQL Server 行级锁、锁升级
Lock与Latch的区别
- 对象:事务/线程
- 保护:数据库对象/内存结构对象
- 持续时间:长/短
- 模式:表锁行锁/互斥
- 死锁:有/无
InnoDB存储引擎中锁
- 表级
- IS 意向共享锁
- IX 意向排它锁
- 行级
- S 行级共享锁
- X 行级排它锁
update更新一行时,会在要更新的表上加IX锁,并在更新的行上加X锁,这时如果并发有用户drop table,看到表上有IX锁,就会立即报错
InnoDB row lock(行锁)范围
- Record lock:行记录锁
- Gap lock:间隙锁,在索引记录间隙上的锁,或者是第一条索引记录之前、最后一条索引记录之后上的间隙锁,只有隔离级别为Repeatable Read的普通索引才有Gap lock
- Next-key lock:下一键锁,索引记录锁以及索引记录之间的间隙锁,前二者的组合锁
测试Record Lock
# 创建测试表 create table t2(id int, name varchar(10),primary key(id),key(name)); insert into t2 values (1,'A'),(3,'A'),(5,'C'),(7,'G'),(10,'I'); commit; select id,name from t2; +----+------+ | id | name | +----+------+ | 1 | A | | 3 | A | | 5 | C | | 7 | G | | 10 | I | +----+------+ # 测试一 # session 1: begin; select * from t2 where name='C' for update; # session 2: begin; select * from t2 where id=5 lock in share mode; #这时session 2被阻塞,查看锁信息 select * from information_schema.innodb_locks; +--------------+-------------+-----------+-----------+------------+------------+------------+-----------+----------+-----------+ | lock_id | lock_trx_id | lock_mode | lock_type | lock_table | lock_index | lock_space | lock_page | lock_rec | lock_data | +--------------+-------------+-----------+-----------+------------+------------+------------+-----------+----------+-----------+ | 14789:19:3:4 | 14789 | S | RECORD | `lyj`.`t2` | PRIMARY | 19 | 3 | 4 | 5 | | 14788:19:3:4 | 14788 | X | RECORD | `lyj`.`t2` | PRIMARY | 19 | 3 | 4 | 5 | +--------------+-------------+-----------+-----------+------------+------------+------------+-----------+----------+-----------+ # 测试二 # session 1: begin; select * from t2 where id=5 and name='C' for update; # session 2: begin; select * from t2 where id=5 and name='B' for update; #这时session 2被阻塞,查看锁信息 select * from information_schema.innodb_locks; +--------------+-------------+-----------+-----------+------------+------------+------------+-----------+----------+-----------+ | lock_id | lock_trx_id | lock_mode | lock_type | lock_table | lock_index | lock_space | lock_page | lock_rec | lock_data | +--------------+-------------+-----------+-----------+------------+------------+------------+-----------+----------+-----------+ | 14793:19:3:4 | 14793 | X | RECORD | `lyj`.`t2` | PRIMARY | 19 | 3 | 4 | 5 | | 14792:19:3:4 | 14792 | X | RECORD | `lyj`.`t2` | PRIMARY | 19 | 3 | 4 | 5 | +--------------+-------------+-----------+-----------+------------+------------+------------+-----------+----------+-----------+ |
测试GAP LOCK
# 测试一 # session 1 set tx_isolation='repeatable-read'; begin; select * from t2 where name='C' for update; # session 2 set tx_isolation='repeatable-read'; begin; insert into t2 values (6,'C'); #这时session 2被阻塞,查看锁信息以下几种方法: show engine innodb status\G; select * from information_schema.innodb_locks; +--------------+-------------+-----------+-----------+------------+------------+------------+-----------+----------+-----------+ | lock_id | lock_trx_id | lock_mode | lock_type | lock_table | lock_index | lock_space | lock_page | lock_rec | lock_data | +--------------+-------------+-----------+-----------+------------+------------+------------+-----------+----------+-----------+ | 14814:19:4:5 | 14814 | X,GAP | RECORD | `lyj`.`t2` | name | 19 | 4 | 5 | 'G', 7 | | 14813:19:4:5 | 14813 | X,GAP | RECORD | `lyj`.`t2` | name | 19 | 4 | 5 | 'G', 7 | +--------------+-------------+-----------+-----------+------------+------------+------------+-----------+----------+-----------+ SELECT r.trx_id waiting_trx_id, r.trx_mysql_thread_id waiting_thread, r.trx_query waiting_query, b.trx_id blocking_trx_id, b.trx_mysql_thread_id blocking_thread, b.trx_query blocking_query FROM information_schema.innodb_lock_waits w INNER JOIN information_schema.innodb_trx b on b.trx_id=w.blocking_trx_id INNER JOIN information_schema.innodb_trx r on r.trx_id=w.requesting_trx_id; +----------------+----------------+-------------------------------+-----------------+-----------------+----------------+ | waiting_trx_id | waiting_thread | waiting_query | blocking_trx_id | blocking_thread | blocking_query | +----------------+----------------+-------------------------------+-----------------+-----------------+----------------+ | 14819 | 30 | insert into t2 values (6,'C') | 14813 | 32 | NULL | +----------------+----------------+-------------------------------+-----------------+-----------------+----------------+ SELECT p2.`HOST` Blockedhost, p2.`USER` BlockedUser, r.trx_id BlockedTrxId, r.trx_mysql_thread_id BlockedThreadId, TIMESTAMPDIFF( SECOND, r.trx_wait_started, CURRENT_TIMESTAMP ) WaitTime, r.trx_query BlockedQuery, l.lock_table BlockedTable, m.`lock_mode` BlockedLockMode, m.`lock_type` BlockedLockType, m.`lock_index` BlockedLockIndex, m.`lock_space` BlockedLockSpace, m.lock_page BlockedLockPage, m.lock_rec BlockedLockRec, m.lock_data BlockedLockData, p.`HOST` blocking_host, p.`USER` blocking_user, b.trx_id BlockingTrxid, b.trx_mysql_thread_id BlockingThreadId, b.trx_query BlockingQuery, l.`lock_mode` BlockingLockMode, l.`lock_type` BlockingLockType, l.`lock_index` BlockingLockIndex, l.`lock_space` BlockingLockSpace, l.lock_page BlockingLockPage, l.lock_rec BlockingLockRec, l.lock_data BlockingLockData, IF (p.COMMAND = 'Sleep', CONCAT(p.TIME,' seconds'), 0) idel_in_trx FROM information_schema.INNODB_LOCK_WAITS w INNER JOIN information_schema.INNODB_TRX b ON b.trx_id = w.blocking_trx_id INNER JOIN information_schema.INNODB_TRX r ON r.trx_id = w.requesting_trx_id INNER JOIN information_schema.INNODB_LOCKS l ON w.blocking_lock_id = l.lock_id AND l.`lock_trx_id`=b.`trx_id` INNER JOIN information_schema.INNODB_LOCKS m ON m.`lock_id`=w.`requested_lock_id` AND m.`lock_trx_id`=r.`trx_id` INNER JOIN information_schema. PROCESSLIST p ON p.ID = b.trx_mysql_thread_id INNER JOIN information_schema. PROCESSLIST p2 ON p2.ID = r.trx_mysql_thread_id ORDER BY WaitTime DESC \G; |
分析一条SQL会加哪些锁
set tx_isolation='repeatable-read'; create table t4 ( id int(11) not null default '0', user_id int(11) default null, user_name varchar(10) default null, create_time varchar(10) default null, address varchar(10) default null, primary key (id), key idx_time_name (create_time,user_name) ); insert into t4 values (1,101,'tom','20161010',''), (4,104,'joe','20160305',''), (6,106,'tom','20161231',''), (8,108,'tom','20160515','sh'), (10,110,'tom','20160101',''), (100,200,'jack','20161120',''); commit; select * from t4 where create_time>'20160101' and create_time<'20161120' and user_name='tom' and address!='' for update; |
下图为执行上面SQL语句后会加哪些锁的图示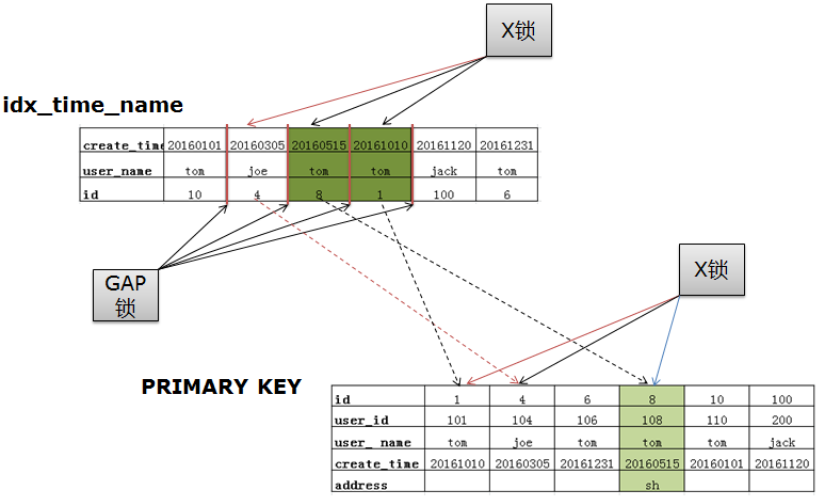
MDL锁
Mysql5.5版本引入了MDL锁(metadata lock),用于解决或者保证DDL操作与DML操作之间的一致性。
在mysqldump的时候不能做DDL操作,会提示wailing for table metadata lock;在做DDL操作没办法保护事务,因此引入了meta data lock。
# session 1 begin; select * from t1; # session 2 drop table t1; #这时session 2被阻塞,可以通过以下命令查看状态 show processlist; +----+------+-----------+------+---------+------+---------------------------------+------------------+ | Id | User | Host | db | Command | Time | State | Info | +----+------+-----------+------+---------+------+---------------------------------+------------------+ | 38 | root | localhost | lyj | Sleep | 155 | | NULL | | 39 | root | localhost | lyj | Query | 115 | Waiting for table metadata lock | drop table t1 | # 这个就是meta data lock | 40 | root | localhost | NULL | Query | 0 | init | show processlist | +----+------+-----------+------+---------+------+---------------------------------+------------------+ |
解决meta data lock的策略:
- 解决DDL高并发
- 线上DB不要轻易做alter table
- 干掉DDL会话
show processlist;kill id;
死锁的原理与分析
- 产生回路
两个或两个以上的事务执行过程中,分别持有一把锁,然后加另一把锁(AB-BA),产生死锁。 - 加锁顺序不一致
两个或两个以上的事务并发执行(同一时刻),因争夺锁资源而造成的一种互相等待,产生死锁。
场景:产生回路导致死锁测试
select * from t1; +------+-------+ | id | name | +------+-------+ | 1 | aaaaa | | 2 | aaaaa | | 3 | cccc | | 5 | eeeee | +------+-------+ # session 1 begin; update t1 set name='AAAAA' where id=1; # session 2 begin; update t1 set name='BBBBB' where id=2; # session 1 update t1 set name='CCCCC' where id=2; # 这时操作会被阻塞 # session 2 begin; update t1 set name='DDDDD' where id=1; ERROR 1213 (40001): Deadlock found when trying to get lock; try restarting transaction # 这时session 2会报死锁错误,操作被rollback; 而session 1的事务阻塞解除, # session 1 select * from t1; +------+-------+ | id | name | +------+-------+ | 1 | AAAAA | | 2 | CCCCC | | 3 | cccc | | 5 | eeeee | +------+-------+ # session 2 select * from t1; +------+-------+ | id | name | +------+-------+ | 1 | aaaaa | | 2 | aaaaa | | 3 | cccc | | 5 | eeeee | +------+-------+ # 可以通过以下命令查看最后一次死锁解撤的信息: show engine innodb status\G; ------------------------ LATEST DETECTED DEADLOCK ------------------------ 2017-03-10 14:47:38 7f150d11a700 *** (1) TRANSACTION: TRANSACTION 14866, ACTIVE 63 sec fetching rows mysql tables in use 1, locked 1 LOCK WAIT 3 lock struct(s), heap size 1184, 2 row lock(s), undo log entries 1 MySQL thread id 38, OS thread handle 0x7f150d0d9700, query id 1579 localhost root updating update t1 set name='CCCCC' where id=2 *** (1) WAITING FOR THIS LOCK TO BE GRANTED: RECORD LOCKS space id 18 page no 3 n bits 80 index `GEN_CLUST_INDEX` of table `lyj`.`t1` trx id 14866 lock_mode X locks rec but not gap waiting Record lock, heap no 8 PHYSICAL RECORD: n_fields 5; compact format; info bits 0 0: len 6; hex 000000501013; asc P ;; 1: len 6; hex 000000003a13; asc : ;; 2: len 7; hex 3c0000093b0110; asc < ; ;; 3: len 4; hex 80000002; asc ;; 4: len 5; hex 4242424242; asc BBBBB;; ...... # innodb_print_all_deadlocks设置为ON时,会把死锁的信息记录到错误日志里 show variables like '%dead%'; +----------------------------+-------+ | Variable_name | Value | +----------------------------+-------+ | innodb_print_all_deadlocks | OFF | +----------------------------+-------+ set global innodb_print_all_deadlocks='ON'; |
减少Innodb死锁的方法
- 超时设置(参数
innodb_lock_wait_timout) - 尽快提交事务,小事务不容易发生死锁
- 加
FOR UPDATE、LOCK IN SHARE NODE读锁时,最好降低事务隔离级别,例如用RC级别,降低死锁发生概率 - 事务中涉及多个表,或者涉及多行记录时,每个事务的操作顺序都要保持一致,降低死锁概率,最好用存储过程/存储函数固化
- 通过索引等方式优化SQL效率,降低死锁发生概率(减少扫描/锁范围,降低概率)
查找锁常用命令
#查看innodb引擎 show engine innodb status\G; #查看锁 SELECT r.trx_id waiting_trx_id, r.trx_mysql_thread_id waiting_thread, r.trx_query waiting_query, b.trx_id blocking_trx_id, b.trx_mysql_thread_id blocking_thread, b.trx_query blocking_query FROM information_schema.innodb_lock_waits w INNER JOIN information_schema.innodb_trx b ON b.trx_id= w.blocking_trx_id INNER JOIN information_schema.innodb_trx r ON r.trx_id= w.requesting_trx_id; select * from information_schema.innodb_trx\G; # 表中几个最常用的字段: trx_id: InnoDB存储引擎内部唯一的事务ID trx_state: 当前事务的状态 trx_started: 事务的开始时间 trx_wait_started: 事务等待开始的时间 trx_mysql_thread_id: Mysql中的线程ID,SHOW PROCESSLIST显示的结果 trx_query: 事务运行的sql语句 select * from information_schema.innodb_locks\G; # 表中几个最常用的字段: lock_id: 锁的ID lock_trx_id: 事务ID lock_mode: 锁的模式 lock_type: 锁的类型,表锁还是行锁 lock_table: 要加锁的表 lock_index: 锁的索引 lock_space: InnoDB存储引擎表空间的ID号 lock_page: 被锁住的页的数量。若是表锁,则该值为NULL lock_rec: 被锁住的行的数量。若是表锁,则该值为NULL lock_data: 被锁住的行的主键值。当是表锁时,该值为NULL select * from information_schema.innodb_lock_waits\G; # 表中几个最常用的字段: requesting_trx_id: 申请锁资源的事务ID requesting_lock_id: 申请的锁的ID blocking_trx_id: 阻塞的锁的ID |